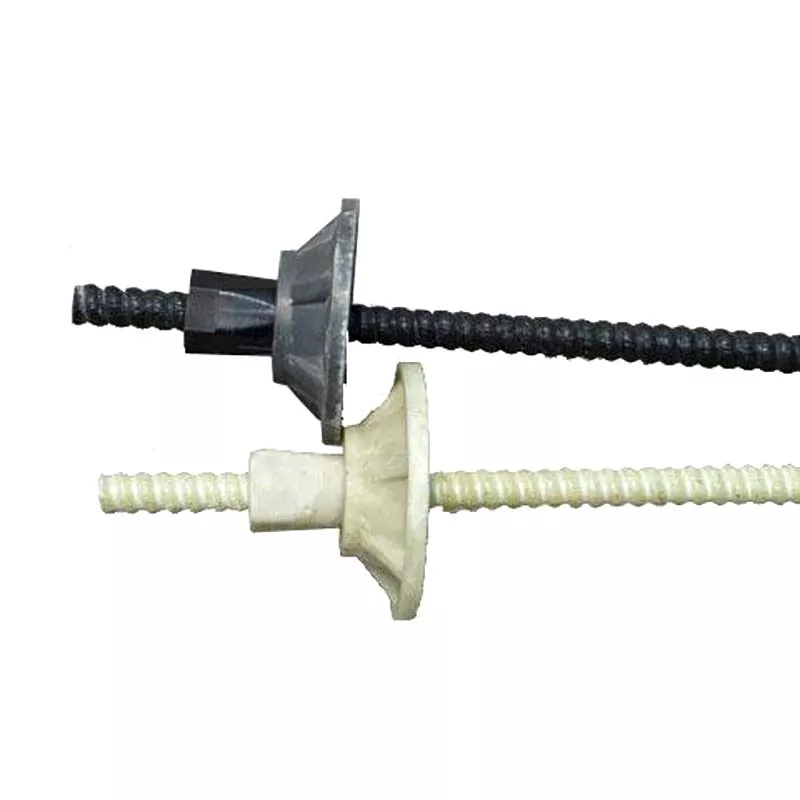
Fiberglass Rockbolt
Fiberglass rockbolt is a reinforcement material used in geotechnical engineering and mine support
Fiberglass rockbolt is a reinforcement material used in geotechnical engineering and mine support, typically made of high-strength fiberglass bundles encapsulated in resin or cementitious matrix. It resembles traditional steel rebar in appearance but is lighter, more corrosion-resistant, and offers excellent mechanical properties. Fiberglass rockbolts are available in round or threaded shapes and can be customized in length and diameter to meet specific project requirements.
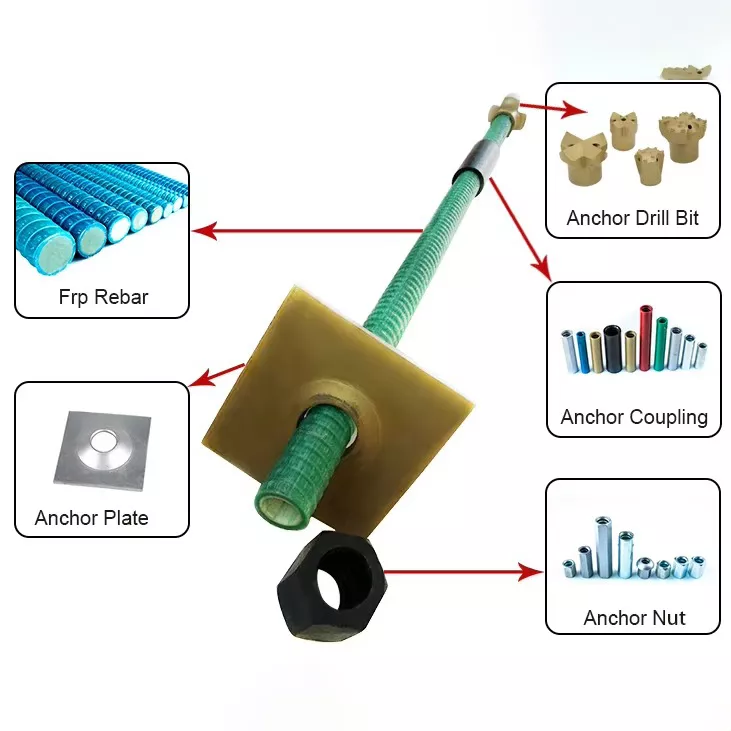
Compared to traditional steel rockbolts, fiberglass rockbolts provide several key advantages:
- Corrosion Resistance: Unaffected by moisture, chemicals, or extreme environments, making them ideal for humid, acidic, alkaline, or salt-laden conditions.
- Lightweight: Significantly lighter than steel rockbolts, making handling, installation, and transportation easier while improving construction efficiency.
- High Strength: Offers excellent tensile strength, comparable to steel, while maintaining good ductility and impact resistance.
- Electrical Insulation: Non-conductive, making it suitable for high-voltage electrical facilities, subways, and mining areas where electromagnetic interference or explosion prevention is required.
- Easy to Cut: Can be cut without sparking, enhancing safety in coal mines or flammable and explosive environments.
With its high strength, lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation,
application in:
1. Tunnel and Mining Support
Fiberglass rockbolts are widely used for roof and wall support in tunnels, underground passages, and mining operations, preventing collapses and ensuring structural stability.
2. Slope and Retaining Wall Reinforcement
- Applied in highway and railway slopes, landslide prevention, enhancing stability and preventing soil erosion or collapses.
- Used for retaining wall anchoring, improving resistance to seismic activities and long-term loads.
3. Foundation and Ground Stabilization
- Ideal for soft soil foundations and loose rock formations, enhancing load-bearing capacity and overall stability.
- Particularly advantageous in marine engineering and wetland foundations, where corrosion resistance outperforms traditional steel reinforcement.
4. Structural Rehabilitation and Infrastructure Repair
- Used in bridges, buildings, and historical structures to provide additional reinforcement and extend service life.
- Applied in post-earthquake reconstruction, reinforcing damaged structures to restore stability.
5. Specialized Applications
- Marine and Coastal Engineering: Suitable for piers, seawalls, offshore wind farm foundations, providing long-term corrosion resistance.
- Underground Utility Tunnels & Nuclear Facilities: Supports pipelines and cables while ensuring structural integrity and minimizing electromagnetic interference.
- High-Voltage Electrical Installations: Due to its non-conductive properties, it is widely used in substations, tunnels, and subway systems where metal rockbolts are not suitable.


